 Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) are widely used for the primary and secondary prevention of venous and arterial thromboembolic events.
Vitamin K antagonists (VKAs) are widely used for the primary and secondary prevention of venous and arterial thromboembolic events.- VKAs, such as warfarin, interfere with the y-carboxylation of the calcium-active binding sites for vitamin K-dependent proteins (including coagulation factors II, VII, IX and X), resulting in the reduction of clotting factors II, VII, IX, X as well as pro-coagulation proteins C and S.
- The most common adverse reaction of warfarin is hemorrhage, accounting for approximately 29,000 emergency department visits per year.
- There are up to 10,000 cases of warfarin-associated intracranial hemorrhage (ICH) in the US annually.
- Patients on warfarin who experience head injury have a 40% higher risk of incurring ICH and a 2-fold higher risk of 30-day in-hospital mortality.
- Gastrointestinal bleeding (GIB) accounts for 30% to 60% of the annual incidence of major bleeding complications, with up to one-third of GIB patients experiencing the first bleeding episode within 1 month of initiating anticoagulation and about 61% of GI bleeds occurring within the first year after initiating anticoagulation.

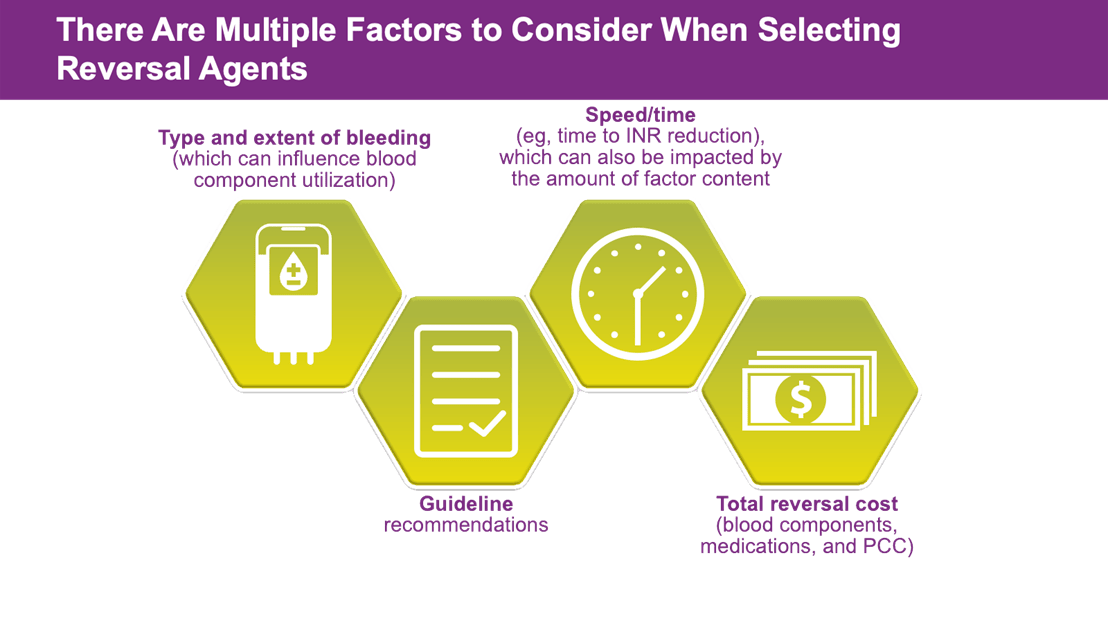
VKA Related Bleeding
Have a Question? Use Our New Chat Feature! Chat with our Medical Information Specialists by clicking on the Chat with us now available in the lower right corner of this screen.
- Warfarin reversal strategies include: fresh frozen plasma (FFP), vitamin K, prothrombin complex concentrates (PCC): (3 Factor PCC, non-activated 4 Factor PCC and activated 4F Factor PCC)
- Kcentra®, Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (Human), is an FDA-approved 4F-PCC for warfarin-related reversal in the setting of acute major bleeding and need for urgent surgery or procedure in adult patients.
- The prothrombin time (PT) test or International Normalized Ratio (INR), which is a standardized expression of the PT, is most commonly used to monitor VKA therapy.
- The most common target INR is 2 to 3 for patients on warfarin; the INR range can vary depending on the indication when on VKA therapy.
- In two pivotal clinical trials, the INR reduction target for VKA reversal was ≤1.3 at 0.5 hours after end of infusion
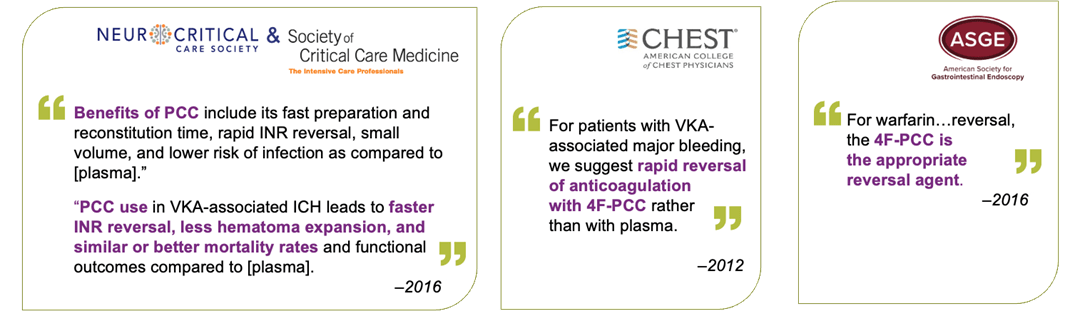
Multiple treatment guidelines recommend the use of 4F-PCC for urgent warfarin reversal in acute major bleeding and need for urgent surgery/invasive procedure including:
- American College of Chest Physicians (ACCP) 2012 and 2018
- American Society of Hematology (ASH) 2018
- American College of Surgeons (ACS) 2018
- American College of Cardiology Consensus Paper
- American College of Emergency Physicians (ACEP)/Annals of Emergency Medicine 2019
- Neurocritical Care Society/Society of Critical Care Medicine 2015
- American Society of Gastrointestinal Endoscopy ASGE 2016
- American Heart Association/American Stroke Association (AHA/ASA) 2022 Guideline for the Management of Patients With Spontaneous Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Important Safety Information for KCENTRA
WARNING: ARTERIAL AND VENOUS THROMBOEMBOLIC COMPLICATIONS
Patients being treated with Vitamin K antagonist therapy have underlying disease states that predispose them to thromboembolic events. Potential benefits of reversing VKA should be weighed against the risk of thromboembolic events, especially in patients with history of such events. Resumption of anticoagulation therapy should be carefully considered once the risk of thromboembolic events outweighs the risk of acute bleeding. Both fatal and nonfatal arterial and venous thromboembolic complications have been reported in clinical trials and postmarketing surveillance. Monitor patients receiving KCENTRA, and inform them of signs and symptoms of thromboembolic events. KCENTRA was not studied in subjects who had a thromboembolic event, myocardial infarction, disseminated intravascular coagulation, cerebral vascular accident, transient ischemic attack, unstable angina pectoris, or severe peripheral vascular disease within the prior 3 months. KCENTRA might not be suitable for patients with thromboembolic events in the prior 3 months.
KCENTRA is contraindicated in patients with known anaphylactic or severe systemic reactions to KCENTRA or any of its components (including heparin, Factors II, VII, IX, X, Proteins C and S, Antithrombin III and human albumin). KCENTRA is also contraindicated in patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Because KCENTRA contains heparin, it is contraindicated in patients with heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT).
Hypersensitivity reactions to KCENTRA may occur. If patient experiences severe allergic or anaphylactic type reactions, discontinue administration and institute appropriate treatment.
In clinical trials, the most frequent (≥2.8%) adverse reactions observed in subjects receiving KCENTRA were headache, nausea/vomiting, hypotension, and anemia. The most serious adverse reactions were thromboembolic events, including stroke, pulmonary embolism and deep vein thrombosis.
KCENTRA is derived from human plasma. The risk of transmission of infectious agents, including viruses and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent and its variant (vCJD), cannot be completely eliminated.
Indications for KCENTRA
KCENTRA®, Prothrombin Complex Concentrate (Human), is a blood coagulation factor replacement product indicated for the urgent reversal of acquired coagulation factor deficiency induced by Vitamin K antagonist (VKA—eg, warfarin) therapy in adult patients with acute major bleeding or the need for urgent surgery or other invasive procedure. KCENTRA is for intravenous use only.
Please see full prescribing information for KCENTRA.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact the CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.



