Primary Immune Deficiency (PID)
Have a Question? Use Our New Chat Feature! Chat with our Medical Information Specialists by clicking on the Chat with us now available in the lower right corner of this screen.
Educational Materials
PID Shared Decision Making Tool
IgG Mechanism of Action
Manufacturing Process - Immunoaffinity Chromatography
Meet the Experts
Dr Jen Heimall: PID path to diagnosis
Dr Shahzad Mustafa: IgRT for management of Immunodeficiency
Janet R: Patient perspective on simplifying PID diagnosis and treatment
Dr Patricia Lugar: Chronic rhinosinusitis and Unmasking PID
Dr Antoine Azar: The unmasking of primary immunodeficiencies through pulmonary disease
Important Safety Information for Hizentra
WARNING: Thrombosis may occur with immune globulin products, including Hizentra. Risk factors may include: advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors.
For patients at risk of thrombosis, administer Hizentra at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity.
Hizentra is contraindicated in patients with a history of anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to human immune globulin (Ig) or components of Hizentra (eg, polysorbate 80), as well as in patients with immunoglobulin A deficiency with antibodies against IgA and a history of hypersensitivity. Because Hizentra contains L-proline as stabilizer, use in patients with hyperprolinemia is contraindicated.
IgA-deficient patients with anti-IgA antibodies are at greater risk of severe hypersensitivity and anaphylactic reactions. Thrombosis may occur following treatment with Ig products, including Hizentra.
Monitor patients for aseptic meningitis syndrome (AMS), which may occur following treatment with Ig products, including Hizentra. In patients at risk of acute renal failure, monitor renal function, including blood urea nitrogen, serum creatinine and urine output. In addition, monitor patients for clinical signs of hemolysis or pulmonary adverse reactions (eg, transfusion-related acute lung injury [TRALI]).
Hizentra is derived from human blood. The risk of transmission of infectious agents, including viruses and, theoretically, the Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (CJD) agent and its variant (vCJD), cannot be completely eliminated.
The most common adverse reactions (observed in ≥5% of study subjects) were local infusion-site reactions, as well as headache, diarrhea, fatigue, back pain, nausea, extremity pain, cough, upper respiratory tract infection, rash, pruritus, vomiting, upper abdominal pain, migraine, arthralgia, pain, fall, and nasopharyngitis.
The passive transfer of antibodies can interfere with response to live virus vaccines and lead to misinterpretation of serologic test results.
Indications for Hizentra
Hizentra®, Immune Globulin Subcutaneous (Human), 20% Liquid, is indicated for:
- Treatment of primary immunodeficiency (PI) in adults and pediatric patients 2 years and older.
- Maintenance therapy in adults with chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) to prevent relapse of neuromuscular disability and impairment.
- Limitation of Use: Maintenance therapy in CIDP has been systematically studied for 6 months and for a further 12 months in a follow-up study. Continued maintenance beyond these periods should be individualized based on patient response and need for continued therapy.
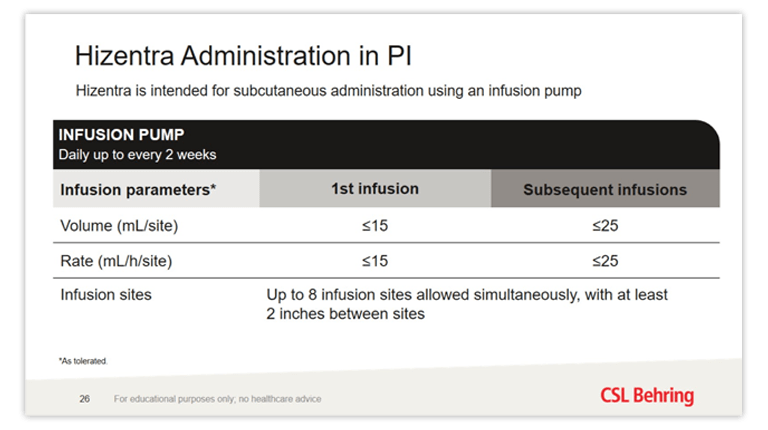
For subcutaneous infusion only.
Please see full prescribing information for Hizentra including boxed warning.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact the CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
Important Safety Information for Privigen
WARNING: THROMBOSIS, RENAL DYSFUNCTION AND ACUTE RENAL FAILURE
- Thrombosis may occur with immune globulin products, including Privigen. Risk factors may include advanced age, prolonged immobilization, hypercoagulable conditions, history of venous or arterial thrombosis, use of estrogens, indwelling vascular catheters, hyperviscosity, and cardiovascular risk factors.
- Renal dysfunction, acute renal failure, osmotic nephrosis, and death may occur with immune globulin intravenous (IGIV) products in predisposed patients. Renal dysfunction and acute renal failure occur more commonly in patients receiving IGIV products that contain sucrose. Privigen does not contain sucrose.
- For patients at risk of thrombosis, renal dysfunction or renal failure, administer Privigen at the minimum dose and infusion rate practicable. Ensure adequate hydration in patients before administration. Monitor for signs and symptoms of thrombosis and assess blood viscosity in patients at risk for hyperviscosity.
See full prescribing information for complete boxed warning.
Privigen is contraindicated in patients with history of anaphylactic or severe systemic reaction to human immune globulin, in patients with hyperprolinemia, and in IgA-deficient patients with antibodies to IgA and a history of hypersensitivity.
Monitor renal function in patients at risk of developing renal failure. In patients 65 years or older, or in any patient at risk of developing renal insufficiency, do not exceed recommended dose and infuse at the minimum rate practicable.
Hyperproteinemia, hyperviscosity, or hyponatremia may occur with Privigen. Aseptic meningitis syndrome (AMS) may occur—especially with high doses or rapid infusion.
Hemolysis, either intravascular or due to enhanced red blood cell sequestration, may occur. Risk factors include non-O blood group and high doses. Closely monitor patients for hemolysis and hemolytic anemia.
During and shortly following Privigen infusion, elevations of blood pressure (including cases of hypertensive urgency) have been observed.
Monitor patients for pulmonary adverse reactions (transfusion-related acute lung injury [TRALI]).
Privigen is made from human blood and may contain infectious agents.
In clinical studies of patients with PI, the most common adverse reactions to Privigen, observed in >5% of subjects, were headache, fatigue, nausea, chills, vomiting, back pain, pain, elevated body temperature, abdominal pain, diarrhea, cough, stomach discomfort, chest pain, joint swelling/effusion, influenza-like illness, pharyngolaryngeal pain, urticaria, and dizziness.
In clinical studies of patients being treated for chronic ITP, the most common adverse reactions, seen in >5% of subjects, were laboratory findings consistent with hemolysis, headache, elevated body temperature, anemia, nausea, and vomiting.
In clinical studies of patients being treated for CIDP, the most common adverse reactions, observed in >5% of subjects, were headache, asthenia, hypertension, nausea, pain in extremity, hemolysis, influenza-like illness, leukopenia, and rash.
The passive transfer of antibodies that occurs with Privigen treatment may interfere with a patient’s response to live virus vaccines and may lead to misinterpretation of serologic testing.
Indications for Privigen
Privigen is indicated for the treatment of:
- Primary humoral immunodeficiency (PI)
- Chronic immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP) in patients aged 15 years and older
- Chronic inflammatory demyelinating polyneuropathy (CIDP) in adults
- Limitation of use: maintenance therapy in CIDP has not been studied for periods longer than 6 months. Individualize duration of treatment beyond 6 months based on patient response.
Please see full prescribing information for Privigen.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact the CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.