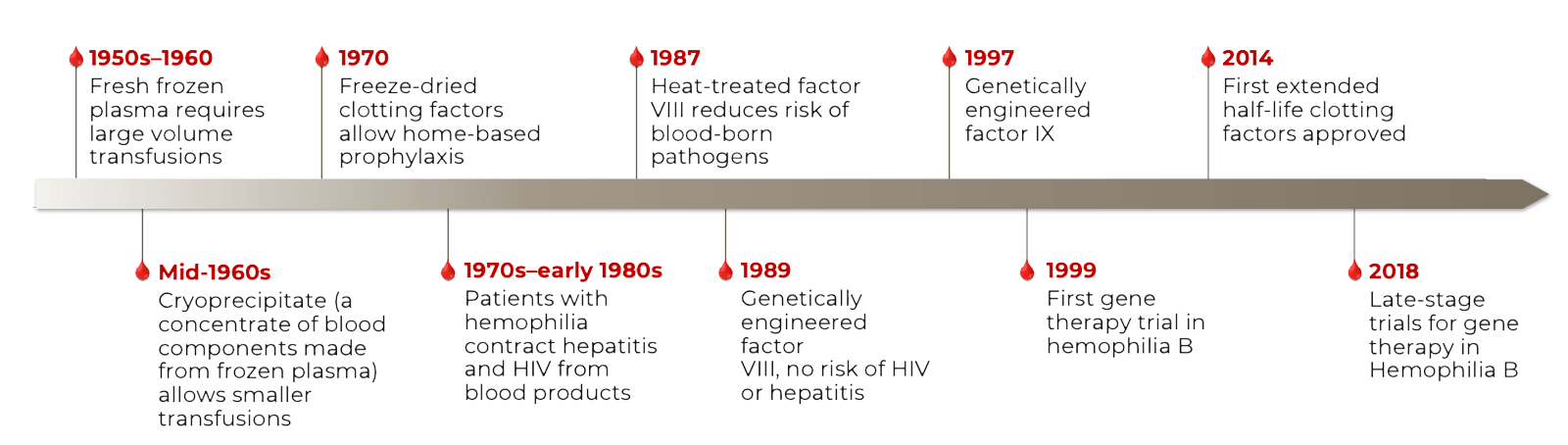
Factor Replacement Therapy

Have a Question? Use Our New Chat Feature! Chat with our Medical Information Specialists by clicking on the Chat with us now available in the lower right corner of this screen.
Factor Replacement Therapy

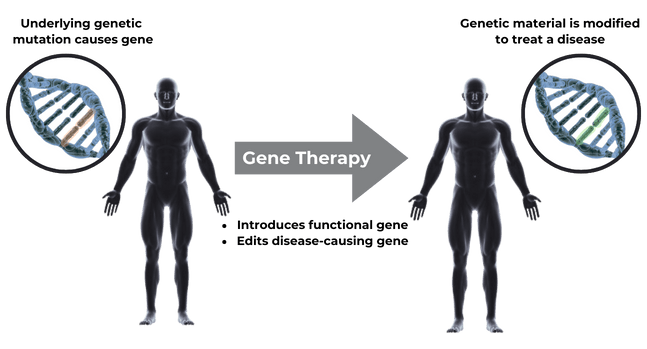
Gene therapy is a transformative treatment that addresses underlying genetic mutations to treat a disease, with several agents already approved for use1,2

AAV Vectors Are Derived From Wild-type AAV
Batty P and Lillicrap D. HemaSphere 2021;5:3(e540); Nathwani AC. Am Soc Hematol Educ Program. 2019;1-8.
Key Similarities and Differences of Hemophilia A and Hemophilia B
 |
CLINICAL SYMPTOMS AND SEVERITY
|
|---|---|
 |
MOLECULAR BASIS OF DISEASE
|
 |
GENE THERAPY VECTOR DESIGN
|
AAV=adeno-associated virus; cDNA=complementary DNA; FI= factor IX; FVIII=factor VIII; PWHA=people with hemophilia A; PWHB=people with hemophilia B.
1. Castaman G, Matino D.Haematologica 2019; 104:1702–1709 2. Batty P, Lillicrap D.HemaSphere 2021; 5:3(e540)
Infusion Reactions
Infusion reactions, including hypersensitivity reactions and anaphylaxis, may occur. Monitor during administration and for at least 3 hours after end of infusion. If symptoms occur, slow or interrupt administration. Re-start administration at a slower infusion once resolved.
Hepatotoxicity/Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Post-dose, monitor for elevated transaminase levels. Consider corticosteroid treatment should elevations occur. The integration of liver-targeting AAV vector DNA into the genome may carry the theoretical risk of hepatocellular carcinoma development. For patients with preexisting risk factors for hepatocellular carcinogenicity, perform regular (eg, annual) abdominal ultrasound and alpha-fetoprotein testing following administration.
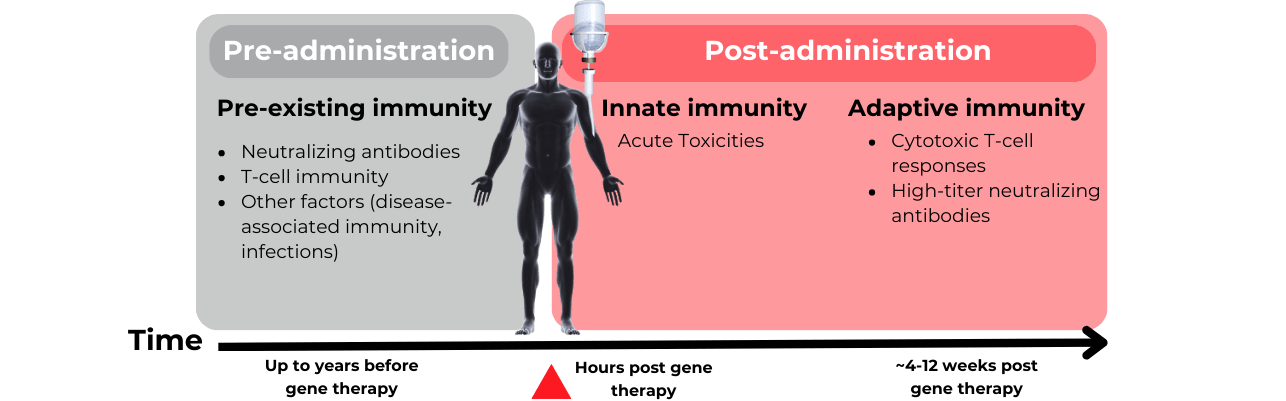
Immune-mediated neutralization of the AAV5 vector capsid
Preexisting neutralizing anti-AAV antibodies may impede transgene expression at desired levels.
Monitoring Laboratory Tests
In addition to monitoring liver function, monitor for Factor IX activity and Factor IX inhibitors after administration.
Adverse ReactionsThe most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥5%) were elevated ALT, headache, blood creatine kinase elevations, flu-like symptoms, infusion-related reactions, fatigue, nausea, malaise, and elevated AST.
HEMGENIX®, etranacogene dezaparvovec-drlb, is an adeno-associated virus vector-based gene therapy indicated for the treatment of adults with Hemophilia B (congenital Factor IX deficiency) who:
HEMGENIX is for single use intravenous infusion only.
Contraindications: None.Please see full prescribing information for HEMGENIX.
To report SUSPECTED ADVERSE REACTIONS, contact the CSL Behring Pharmacovigilance Department at 1-866-915-6958 or FDA at 1-800-FDA-1088 or www.fda.gov/medwatch.
The purpose of this CSL Behring Medical Affairs website is to support U.S. Healthcare Professionals with scientific information. This website is also a channel for U.S. Healthcare Professionals to submit questions or connect with CSL Behring U.S. Healthcare Professionals. The information provided is for educational purposes only and is not intended to promote any products. By continuing to use this site you are acknowledging that you are a U.S. Healthcare Professional